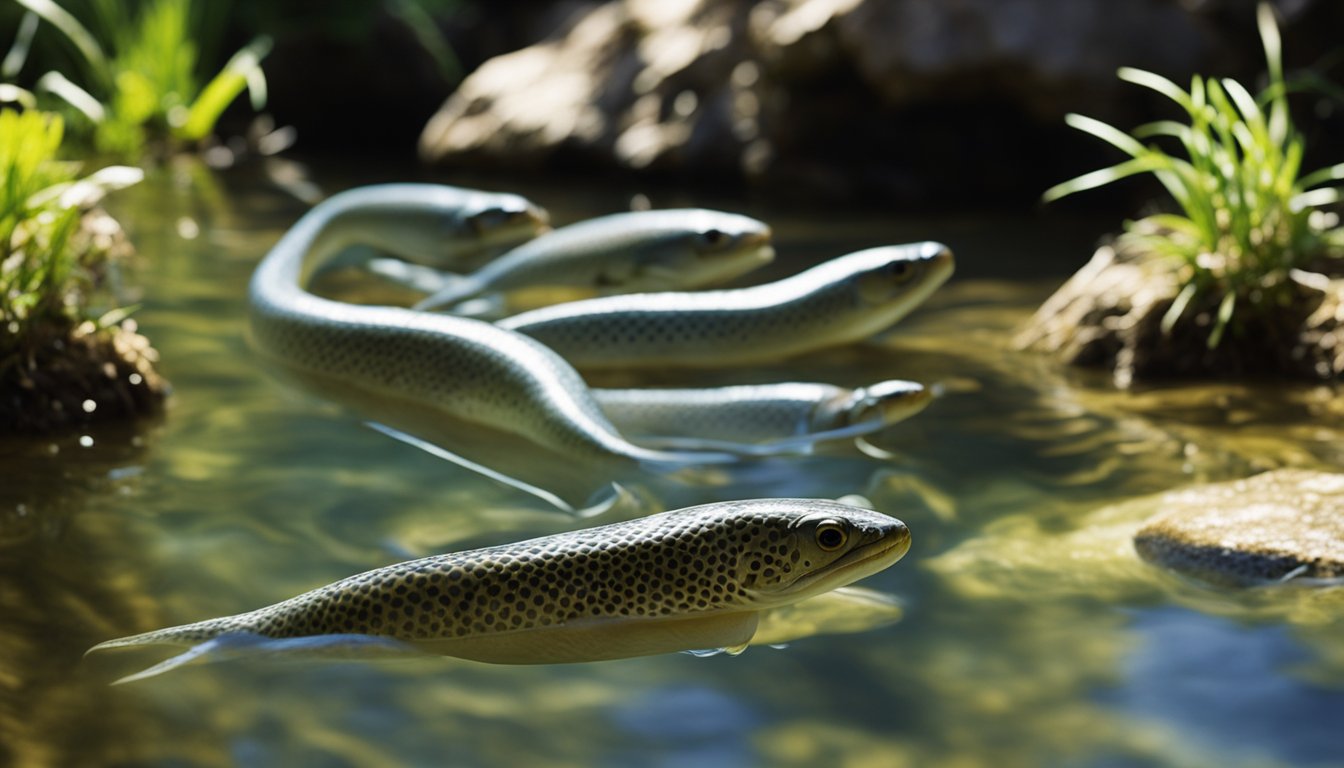
Serpents of the Sea: The Eel’s Journey Between Fresh and Salt Water is a fascinating topic that has puzzled scientists for years.
This elusive creature spends most of its life in freshwater rivers, only to migrate to the ocean to spawn.
But how does it survive in such different environments? What adaptations does it have to make to thrive in both?

One of the most remarkable things about eels is their ability to travel long distances between freshwater and saltwater habitats.
They are able to navigate through complex river systems and even climb up waterfalls to reach their breeding grounds in the ocean.
Once they reach the sea, their bodies undergo a remarkable transformation, adapting to the saltier water and changing their color and behavior.
Despite being one of the most mysterious creatures in the ocean, eels play a vital role in the ecosystem.
They are an important food source for many animals, including humans, and their migration patterns help to distribute nutrients and energy throughout different habitats.
In this article, we will explore the fascinating world of eels and learn about their incredible journey between freshwater and saltwater habitats.
Eel Species Diversity

Eels are a fascinating group of fish that exhibit a wide range of adaptations to their environments.
There are over 800 species of eel, each with its unique characteristics and behaviors.
In this section, we will explore the diversity of eel species, with a focus on their freshwater origins and saltwater adaptations.
Freshwater Origins
Many eel species begin their lives in freshwater environments such as rivers, streams, and lakes.
The larvae of these eels, called leptocephali, are transparent and almost completely flat.
They drift with the ocean currents for months before reaching the freshwater habitats where they will spend most of their lives.
One of the most well-known freshwater eel species is the American eel (Anguilla rostrata).
This eel can be found in rivers and streams along the eastern coast of North America, from Greenland to Venezuela.
The American eel is an important part of many freshwater ecosystems, serving as both predator and prey.
Saltwater Adaptations
While many eel species spend their entire lives in freshwater, others have evolved to thrive in saltwater environments.
These eels have developed unique adaptations to help them survive in the open ocean, including a streamlined body shape and the ability to regulate their salt levels.
One such species is the European eel (Anguilla anguilla).
This eel spends most of its life in the Atlantic Ocean, but migrates to freshwater rivers and streams to spawn.
During its journey, the European eel undergoes a remarkable transformation, developing a darker coloration and a thicker skin to protect it from predators.
In conclusion, eels are a diverse group of fish that have adapted to a wide range of environments.
From their freshwater origins to their saltwater adaptations, eels are a fascinating example of the diversity of life on our planet.
The Eel’s Life Cycle
Reproductive Migration
The eel’s life cycle is a remarkable journey that spans thousands of miles across the ocean.
The eel begins its life in the Sargasso Sea, where it hatches from an egg and spends its early days drifting with ocean currents.
As it matures, the eel undergoes a remarkable transformation, becoming a glass eel and then a yellow eel.
When the eel reaches sexual maturity, it begins a long and arduous journey back to the Sargasso Sea to spawn.
This journey is known as the reproductive migration, and it can take several years to complete.
During this time, the eel travels thousands of miles, navigating through freshwater rivers and streams, and even scaling waterfalls and dams.
The eel’s sense of smell is its primary navigational tool, allowing it to detect the chemical signature of the Sargasso Sea from afar.
Growth and Development
As the eel makes its way back to the Sargasso Sea, it undergoes a final transformation, becoming a silver eel.
This stage is characterized by a change in color and behavior, as the eel prepares for its final journey.
Once the eel reaches the Sargasso Sea, it spawns and dies, completing its life cycle.
The eel’s journey is not just remarkable for its length and complexity, but also for the challenges that the eel must overcome along the way.
From predators to obstacles in its path, the eel faces numerous obstacles that test its strength and resilience.
Despite these challenges, the eel continues to survive and thrive, adapting to its environment and making the most of its remarkable abilities.
In conclusion, the eel’s life cycle is a testament to the power of adaptation and resilience in the face of adversity.
As we continue to learn more about these remarkable creatures, we gain a greater appreciation for the complexity and beauty of the natural world.
Navigational Mysteries

Sensory Abilities
The eel’s journey between fresh and saltwater is a remarkable feat, and one that has puzzled scientists for years.
How do these slippery creatures navigate such vast distances, and how do they find their way back to their birthplace to spawn?
One of the eel’s most impressive abilities is its sense of smell.
Eels have a keen sense of smell, which they use to detect chemical signals in the water.
These signals help them navigate their way through the ocean, and also allow them to detect potential food sources.
Another important sense for eels is their ability to detect changes in the Earth’s magnetic field.
This is known as magnetoreception, and it allows eels to navigate using the Earth’s magnetic field as a compass.
Scientists believe that eels may also use the position of the sun and stars to navigate.
Environmental Challenges
Despite their impressive sensory abilities, eels still face many challenges on their journey between fresh and saltwater.
One of the biggest challenges is the difference in salinity between the two environments.
Eels must be able to adapt to these changes in order to survive.
Another challenge is the presence of man-made obstacles, such as dams and weirs.
These structures can make it difficult for eels to navigate upstream, and can also prevent them from reaching their spawning grounds.
Despite these challenges, eels continue to make their incredible journey each year.
By understanding the navigational mysteries of these fascinating creatures, we can better appreciate the wonders of the natural world.
Conservation Efforts

Human Impact
Human activities such as pollution, habitat destruction, and overfishing have a significant impact on eel populations.
The decline in eel populations has been attributed to the loss of habitat, which is caused by the construction of dams and other barriers that prevent eels from migrating to their breeding grounds.
Pollution from agricultural and industrial activities has also affected the quality of water in which eels live.
Furthermore, overfishing has also been a significant threat to eels. Eels are a delicacy in many countries, and their meat is considered a delicacy.
This has led to overfishing, which has reduced the population of eels in many parts of the world.
The decrease in eel populations has also affected the ecosystem, as eels play a vital role in maintaining the balance of marine and freshwater ecosystems.
Protective Measures
Several measures have been put in place to protect eel populations.
These measures include the construction of eel ladders, which are structures that allow eels to bypass dams and other barriers.
Eel ladders have been successful in restoring eel populations in many areas.
Additionally, there have been efforts to reduce pollution and improve water quality.
Regulations have been put in place to reduce the discharge of pollutants into waterways, and there have been efforts to restore damaged ecosystems.
These measures have helped to improve the quality of water in which eels live.
Furthermore, there have been regulations put in place to reduce overfishing.
These regulations limit the number of eels that can be caught and sold, and they have helped to protect eel populations in many areas.
In conclusion, conservation efforts are necessary to protect eel populations.
Human activities have had a significant impact on eels, and measures must be put in place to protect them.
The construction of eel ladders, the reduction of pollution, and the regulation of fishing are essential steps in protecting eels and maintaining the balance of marine and freshwater ecosystems.
Frequently Asked Questions

What unique journey do eels take between freshwater and saltwater environments?
Eels are known for their remarkable ability to move between freshwater and saltwater environments.
As they grow and mature, they make their way from rivers and streams out to the open ocean, where they eventually reach the Sargasso Sea.
This vast body of water, located in the North Atlantic, is where eels spawn and lay their eggs.
After hatching, the young eels, or elvers, make their way back to freshwater habitats, where they will spend most of their lives.
How does the life cycle of an eel involve the Sargasso Sea?
The Sargasso Sea plays a crucial role in the life cycle of eels.
It is here that adult eels, after spending years in freshwater habitats, make their way to spawn and lay their eggs.
The eggs hatch into tiny, transparent larvae that drift with ocean currents for several months before making their way back to coastal areas.
Once they reach these areas, they transform into glass eels and then elvers, which eventually make their way back to freshwater habitats.
Can you explain the process of eel reproduction in simple terms?
Eels are unique in that they reproduce only once in their lifetime, and only in the Sargasso Sea.
The females release their eggs, which are fertilized by the males.
After hatching, the larvae drift with ocean currents until they reach coastal areas, where they transform into glass eels and then elvers.
The elvers make their way back to freshwater habitats, where they will spend most of their lives.
What are the differences between sea snakes and eels?
While both eels and sea snakes are long, slender, and live in aquatic environments, they are quite different.
Sea snakes are reptiles, while eels are fish.
Sea snakes breathe air and must come to the surface periodically, while eels can extract oxygen from the water using their gills.
Sea snakes are venomous and can be dangerous to humans, while eels are generally not considered dangerous.
Why are eels considered a mystery in the animal kingdom?
Eels have long fascinated scientists and researchers due to their unique life cycle and behavior.
Despite years of research, many aspects of eel biology remain a mystery.
For example, scientists are still unsure how eels navigate from freshwater habitats to the Sargasso Sea to spawn.
Additionally, the exact mechanisms of eel reproduction and development are not yet fully understood.
How do eels adapt to living in both freshwater and marine ecosystems?
Eels are able to adapt to living in both freshwater and marine ecosystems due to their ability to regulate the salt concentration in their bodies.
When in freshwater, eels excrete excess salt through their gills. When in saltwater, they conserve salt by excreting less and drinking more water.
Additionally, eels are able to tolerate a wide range of temperatures and oxygen levels, allowing them to thrive in a variety of aquatic environments.