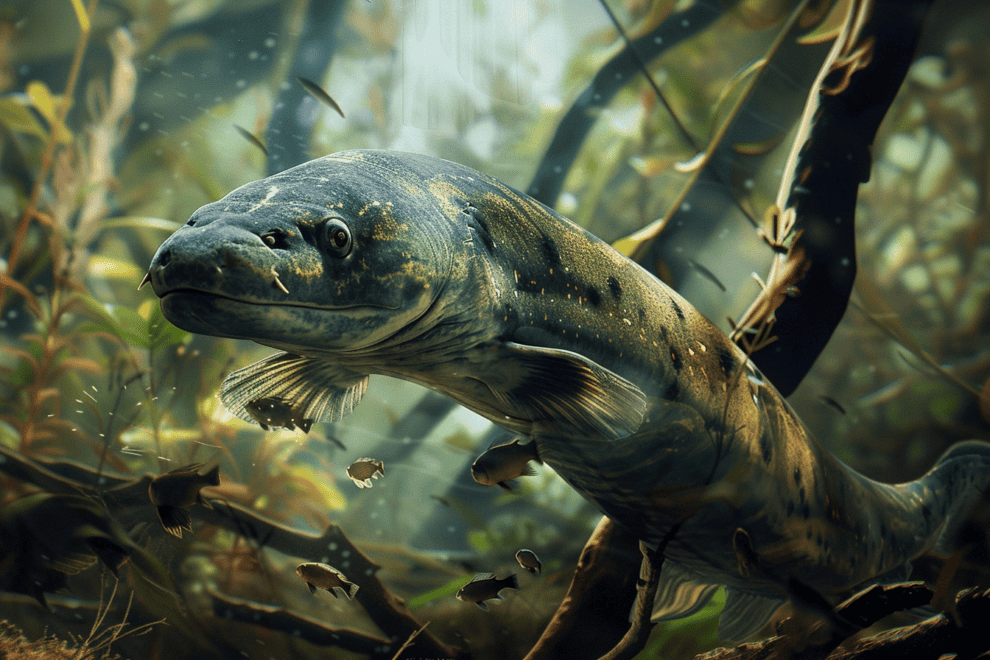
Electric eels in South America’s river basins can generate shocks up to 600 volts using specialized electric organs.
These organs, making up about 80% of their bodies, contain thousands of electrocytes that work like tiny batteries. When hunting or defending, an electric eel discharges these cells simultaneously, delivering a powerful jolt capable of incapacitating prey or deterring threats.
They can even leap out of water to deliver more intense shocks. Besides high-voltage pulses, they also use lower voltage for communication and navigation in murky waters.
Anatomy of Electric Eels
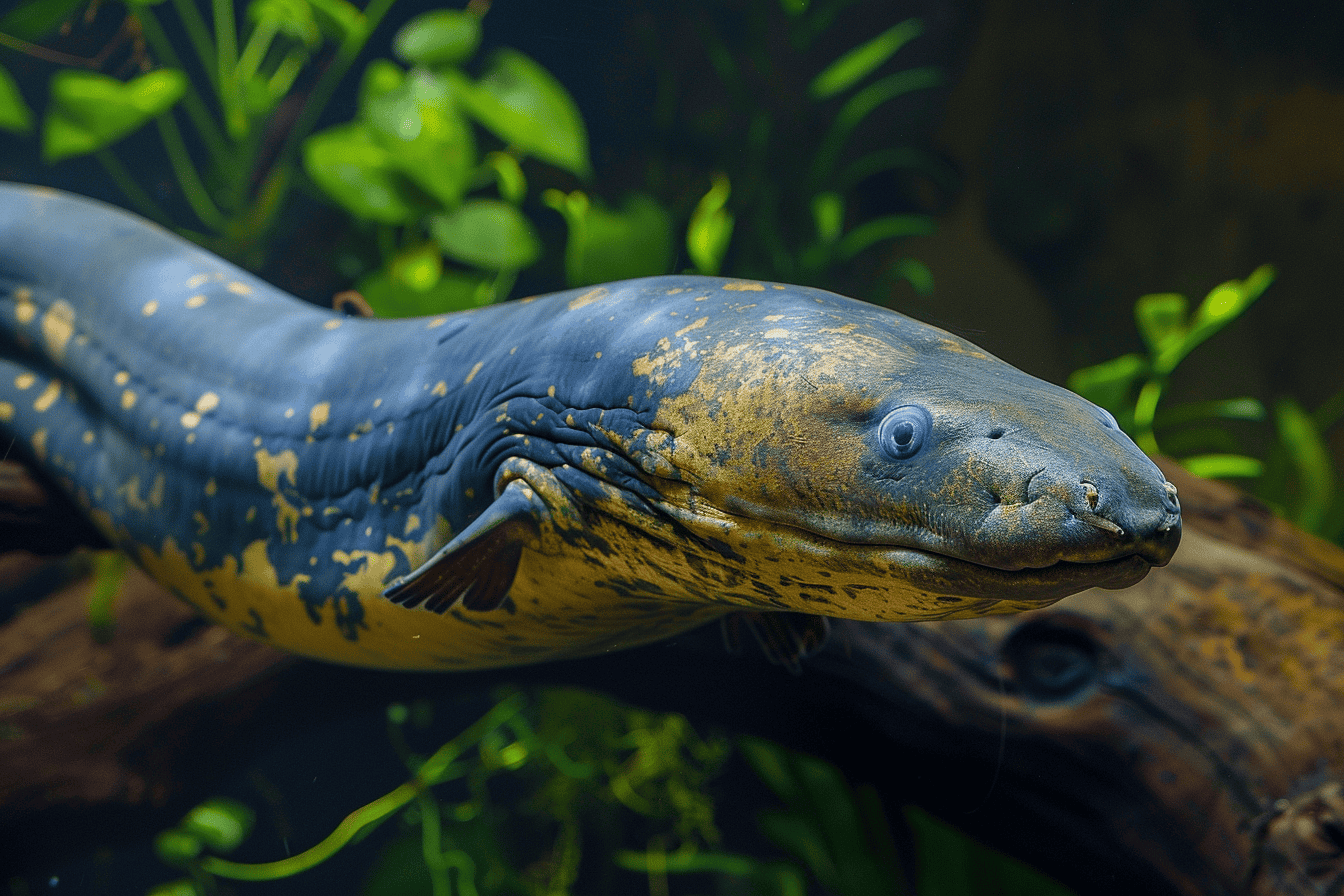

Electric eels have a unique anatomy that allows them to generate powerful electrical charges. These fascinating creatures have electric organs that make up nearly 80% of their bodies. Imagine an eel’s body as a power plant; its electric organs are the generators.
These organs are packed with thousands of specialized cells called electrocytes, each working like a tiny battery to store power.
This ingenious arrangement enables electric eels to harness and release high voltage pulses, reaching up to 600 volts. The simultaneous discharge of these electrocytes creates the impressive electrical shocks that electric eels are famous for.
This capability isn’t just for show; it allows the eel to defend itself and hunt with remarkable efficiency. Imagine the eel’s electric organs as highly sophisticated tools, controlled to deliver shocks of varying intensities.
This adaptability makes them one of the most formidable predators in their ecosystem. When faced with a threat or hunting prey, an electric eel’s ability to generate such high voltage pulses guarantees it remains at the top of the food chain.
How Electric Eels Generate Shocks
Electric eels have specialized cells, known as electrocytes, which make up a staggering 80% of their bodies. These cells act like tiny batteries, storing electrical energy that the eel can release as a potent electric shock.
The electrocytes are stacked in series, enabling the eel to harness electricity efficiently. When the eel decides to discharge, its electrocytes align, generating an electrical charge that can reach up to 600 volts.
Electric eels control the intensity of their shocks, using them for various purposes. They can emit a high-voltage shock for defense or a low-level charge, less than 10 volts, to navigate and locate prey.
The electric organs, composed of modified muscles, span nearly the length of their bodies. Activated by the eel’s motor nerves, these organs allow it to generate and control electricity.
Hunting and Feeding Habits Of Electric Eels
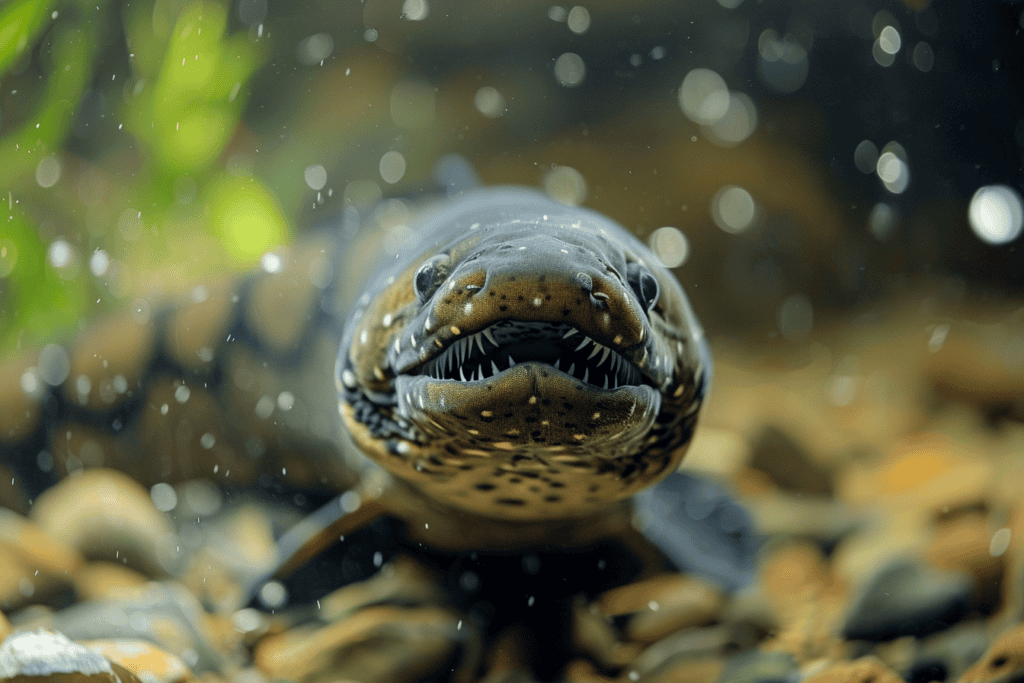

Harnessing their electrifying abilities, electric eels employ high-voltage pulses to incapacitate prey, making hunting an efficient and effective process.
When an eel electric fish detects nearby prey, it releases a powerful burst of electricity. This high-voltage pulse acts like a Taser, causing the prey’s muscles to contract uncontrollably. The electric eel’s pulses activate the nerves leading to the prey fish’s muscles, resulting in a whole-body twitch that immobilizes the prey.
Electric eels often use pairs of high-voltage pulses, known as doublets, to maximize muscle tension in their prey. These doublets, separated by just two milliseconds, are the most effective way to incapacitate prey quickly.
By using doublets, these fascinating electric fish can detect and track prey even in murky waters, making their attack strategy highly efficient. During the hunt, the eel first uses doublets to sense the presence of prey. Once detected, it doesn’t hesitate to attack, sending out more high-voltage pulses to guarantee the prey is completely incapacitated.
How Do Electric Eels Communicate?
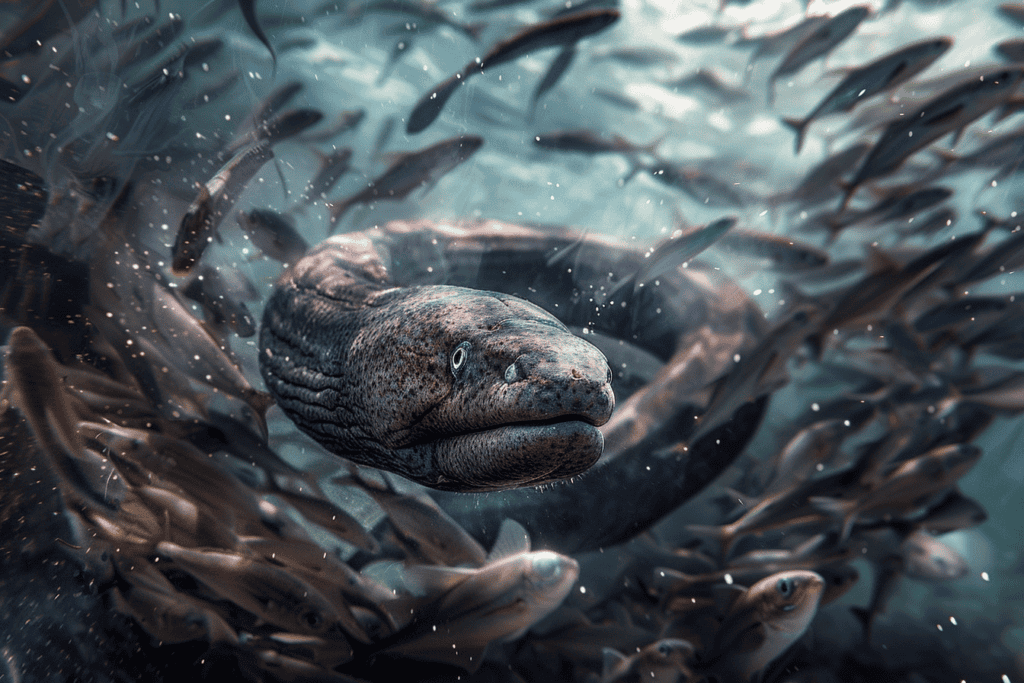

Beyond their impressive hunting skills, electric eels also use low-level electric discharges to communicate and navigate through their murky habitats. These discharges, typically less than 10 volts, help them detect the faint electrical signals generated by other animals. By controlling the intensity, frequency, and duration of these discharges, electric eels can convey different information, making their communication quite sophisticated.
Electric eels have specialized cells called electrocytes that generate these electrical signals. They rely on electroreceptors, specifically the ampullae of Lorenzini, to sense the electric fields around them. This electric sense allows them to build a mental map of their surroundings, helping them navigate even in complete darkness or murky water.
You can imagine how vital this ability is in the dense waters of South America, where visibility is often low.
When it comes to communication, electric eels can detect the presence of other eels and even understand social cues through electrical signals. This electric conversation helps them avoid conflicts, find mates, and maintain social hierarchies.
How Do Eels Interact With Humans
In their interactions with humans, electric eels have sparked both fascination and caution due to their powerful electrical abilities. When you encounter these remarkable creatures, you’re likely to be both amazed and wary.
Kenneth Catania, a biologist renowned for his studies on electric eels, has revealed how these aquatic animals use electricity in surprising ways.
Imagine wading through the waters of South America and suddenly feeling a jolt—this is how an eel’s attack can startle you. These eels use electricity to stun prey, but they can also deliver a high-voltage pulse to deter threats, including curious humans.
Catania’s research found that eels can leap out of the water to press their chins against an intruder, delivering a more intense shock.
The high-voltage pulse, which can reach up to 600 volts, is enough to incapacitate a small animal or cause significant discomfort to a person. So, if you’re exploring their habitats, it’s crucial to respect their space.
While the idea of an electric eel might seem like something from science fiction, their ability to use electricity effectively makes them a true marvel of nature.
Evolutionary History Of Electric Eels

Electric eels have a fascinating evolutionary history that transformed them from weakly electric fish into creatures capable of delivering powerful shocks.
Initially, these fish used low-voltage electricity to probe their surroundings. Over millions of years, they evolved to generate high-voltage pulses, a key adaptation for hunting and defense. This ability to produce electric potential has contributed substantially to their success in South America’s waters.
The Prussian naturalist Alexander von Humboldt was one of the first to document these unique creatures.
Their electric organs, which evolved from muscle tissues, generate electricity through controlled muscle contractions. These organs are activated by the eel’s motor nerves, allowing precise control over the strength and duration of their electric discharges.
This evolutionary history not only shaped their physiology but also their behavior, enabling them to incapacitate prey and fend off predators effectively.
Moreover, electric eels developed unique strategies to overcome the limitations of their electric output.
For instance, they can leap out of the water to attack larger conductors, demonstrating their high adaptability.
This fascinating evolutionary journey from weakly electric fish to powerful shock-producers illustrates the remarkable adaptability and survival mechanisms within the animal kingdom.
Frequently Asked Questions
How Long Do Electric Eels Live in the Wild?
Electric eels in the wild have a lifespan range of 10-15 years. They reach maturity around 7 years, and their growth rate is slower compared to captivity. Their reproductive habits and environmental factors greatly influence their longevity.
Can Electric Eels Survive in Captivity?
Yes, electric eels can survive in captivity, but it’s tough. You need a large tank setup, proper feeding habits, and must address breeding challenges and health issues carefully to guarantee they thrive.
What Are the Natural Predators of Electric Eels?
In electric eel habitats, their natural predators include large fish and caimans. Predator adaptations often include thick skin and strategic attacks. Ecosystem impact is significant, but electric eels’ defensive mechanisms, like high voltage shocks, deter many threats.
Do Electric Eels Pose a Danger to Other Fish in Aquariums?
Yes, electric eels pose a danger to other fish in aquariums. Due to their shock frequency and feeding habits, tank compatibility is low. Prioritize aquarium safety by keeping them separate to prevent harmful discharges.
Are Electric Eels Active During the Day or Night?
Electric eels are most active at night due to their nocturnal habits. Their diurnal activity is minimal, aligning with their sleep patterns. They prefer nighttime feeding times when their prey is also active, optimizing their hunting efficiency.