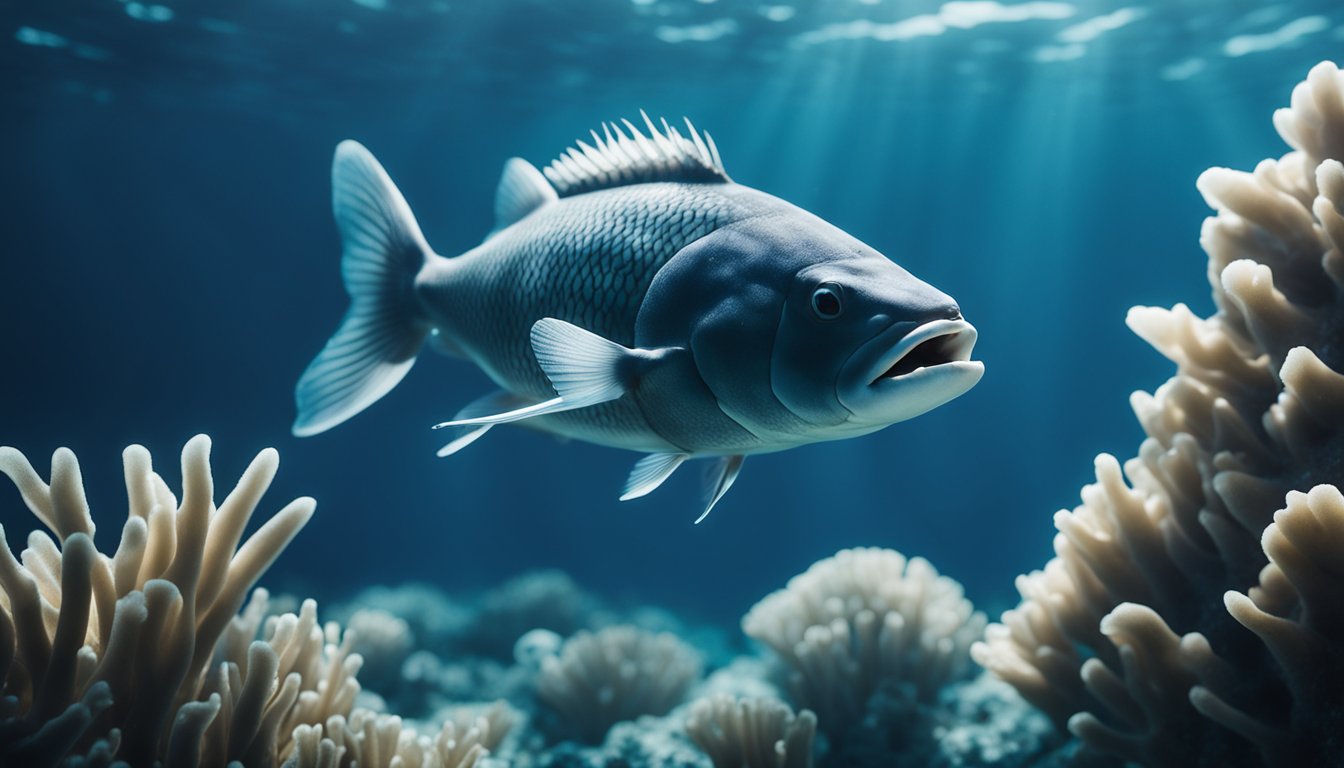
Beneath the icy waters of the Southern Ocean lies a world unlike any other.
Here, in the frozen realm of the Antarctic Toothfish, life thrives in a harsh and unforgiving environment.
This elusive species, also known as the Chilean Seabass, is a prized delicacy in high-end restaurants around the world.
But beyond its culinary appeal, the Toothfish is a fascinating creature with many secrets waiting to be uncovered.

The Antarctic Toothfish is a remarkable animal that has adapted to survive in one of the harshest environments on Earth.
Its habitat is a world of darkness and cold, where temperatures can plummet to -2°C and the water is so salty that it doesn’t freeze.
Despite these extreme conditions, the Toothfish has developed a range of adaptations that allow it to thrive.
Its body is covered in a thick layer of fat that acts as insulation against the cold, and its blood contains a natural antifreeze that prevents it from freezing solid.
These adaptations, along with many others, make the Toothfish a true marvel of evolution.
The Antarctic Toothfish
The Antarctic Toothfish is a mysterious creature that dwells in the frozen waters of the Southern Ocean.
It is a slow-growing, long-lived fish that can reach up to 2 meters in length and weigh over 100 kilograms.
This creature is a top predator in its environment, feeding on other fish, squid, and crustaceans.
Mysterious Behemoths of the Deep
The Antarctic Toothfish is a deep-sea creature that lives at depths of up to 2,000 meters.
Its habitat is one of the most extreme environments on Earth, with subzero temperatures, high pressure, and complete darkness.
Due to the harsh conditions, very little is known about the life cycle and behavior of this creature.
A Life in Subzero Waters
The Antarctic Toothfish has adapted to life in subzero waters by developing unique physiological and behavioral traits.
It has antifreeze proteins in its blood that prevent ice crystals from forming and damaging its cells.
It also has a slow metabolism, which allows it to conserve energy in the cold waters.
The Antarctic Toothfish is a slow-growing species, with a lifespan of up to 50 years.
It reaches sexual maturity at around 12 years of age, and females can lay up to 40,000 eggs per year.
Despite its slow growth, the Antarctic Toothfish is a valuable commercial fishery, with a high demand for its meat in markets around the world.
In conclusion, the Antarctic Toothfish is a fascinating creature that has adapted to life in one of the harshest environments on Earth.
Its mysterious nature and unique adaptations make it an important subject for scientific research and conservation efforts.
The Ecosystem of Ice

The Antarctic toothfish lives in one of the harshest environments on earth, the frozen realm beneath the ice.
This ecosystem is unique and complex, with many different species interacting with each other in a delicate balance.
The Toothfish’s Food Web
The toothfish is a top predator in the Antarctic food web, feeding on a variety of smaller fish and squid.
It has a specialized diet that includes krill, which are tiny shrimp-like creatures that are a staple food for many Antarctic animals.
Krill are abundant in the Southern Ocean, and they form the base of the food web for many species, including whales, seals, and penguins.
The toothfish is able to survive in the harsh Antarctic environment by relying on this rich source of food.
Predators of the Toothfish
Although the toothfish is a top predator in the Antarctic food web, it is not immune to predation itself.
One of its main predators is the Weddell seal, which is able to swim through the icy waters and hunt the toothfish using its powerful jaws.
Other predators of the toothfish include the killer whale and the leopard seal.
These animals are also top predators in the Antarctic ecosystem, and they play an important role in maintaining the balance of the food web.
Overall, the ecosystem of the Antarctic toothfish’s frozen realm is a complex and fascinating environment.
It is home to many different species, each of which plays a vital role in maintaining the delicate balance of this unique ecosystem.
Human Impact and Conservation

Fishing the Elusive Toothfish
The Antarctic Toothfish is a popular delicacy in high-end restaurants around the world, making it a valuable commodity.
Unfortunately, overfishing has threatened the survival of this species.
Toothfish populations have been declining rapidly due to illegal, unreported, and unregulated fishing practices.
The fishing industry has been exploiting the toothfish’s habitat for years, compromising the delicate balance of the Antarctic ecosystem.
Toothfish fishing is regulated by the Commission for the Conservation of Antarctic Marine Living Resources (CCAMLR).
The commission sets catch limits, vessel monitoring systems, and observer programs to ensure sustainable fishing practices.
However, illegal fishing activities still occur, and it is crucial to enforce regulations to protect the toothfish and maintain the health of the Antarctic ecosystem.
Protecting the Polar Giants
The Antarctic Toothfish is not the only species threatened by human activities in the Antarctic.
The region is home to many unique and fragile species, including whales, seals, and penguins.
Climate change, pollution, and overfishing are all contributing factors to the decline of these species.
Conservation efforts are crucial to protect the Antarctic ecosystem and its inhabitants.
The Antarctic Treaty System, an international agreement signed by 54 countries, aims to preserve the region and its resources for peaceful purposes.
The treaty prohibits military activities, mineral mining, and nuclear explosions in the Antarctic.
In addition to the treaty, many organizations and governments are working together to protect the Antarctic ecosystem.
For example, the Antarctic Ocean Alliance is a coalition of environmental organizations advocating for the creation of marine protected areas in the Southern Ocean.
These areas would provide a safe haven for marine life and help preserve the unique Antarctic ecosystem.
It is up to everyone to do their part in protecting the Antarctic ecosystem.
By supporting sustainable fishing practices, reducing pollution, and advocating for conservation efforts, we can ensure the survival of the Antarctic Toothfish and other unique species in the frozen realm.
Frequently Asked Questions

How do toothfish manage to survive in the freezing waters of Antarctica?
The Antarctic toothfish is a remarkable species that can survive in the extreme conditions of the Southern Ocean.
They have several adaptations that enable them to thrive in the freezing waters.
One of these adaptations is their antifreeze proteins, which help prevent their blood from freezing.
They also have a large liver that produces oil, which helps them maintain buoyancy and provides energy during long periods of fasting.
What role does the Antarctic toothfish play in its underwater ecosystem?
The Antarctic toothfish is a top predator in the Southern Ocean and plays a crucial role in the food web.
They feed on smaller fish and squid, and in turn, are preyed upon by larger predators such as killer whales and leopard seals.
Their presence helps maintain a balance in the ecosystem, and their absence could have significant impacts on the entire food chain.
What adaptations do toothfish have that allow them to thrive beneath the ice?
Toothfish have several adaptations that enable them to thrive beneath the ice.
They have a streamlined body shape that allows them to move efficiently through the water, and their large eyes help them see in the low light conditions of the deep ocean.
They also have a slow metabolism, which allows them to conserve energy in the cold water and survive long periods without food.
How do scientists study toothfish in such a harsh and remote environment?
Studying toothfish in their natural habitat is challenging due to the harsh and remote environment of the Southern Ocean.
Scientists use a variety of techniques to study these fish, including acoustic surveys, satellite tagging, and deep-sea submersibles.
They also collect tissue samples and use DNA analysis to understand the genetic diversity of toothfish populations.
What is the life cycle of the Antarctic toothfish, from egg to adult?
The life cycle of the Antarctic toothfish is complex and not well understood.
Females lay eggs in the deep ocean, and the larvae hatch and drift with ocean currents.
The larvae undergo several stages of development before settling on the seafloor as juveniles.
Toothfish can live up to 50 years and do not reach maturity until they are around 10-12 years old.
Why is the Antarctic toothfish important to both local and global marine life?
The Antarctic toothfish is an important species in the Southern Ocean ecosystem and has significant economic value.
It is a valuable fishery resource and is caught for its high-quality meat, which is sold in markets around the world.
However, overfishing and illegal, unreported, and unregulated fishing pose a significant threat to toothfish populations and the ecosystem as a whole.
Protecting toothfish and their habitat is essential for maintaining a healthy and sustainable Southern Ocean ecosystem.