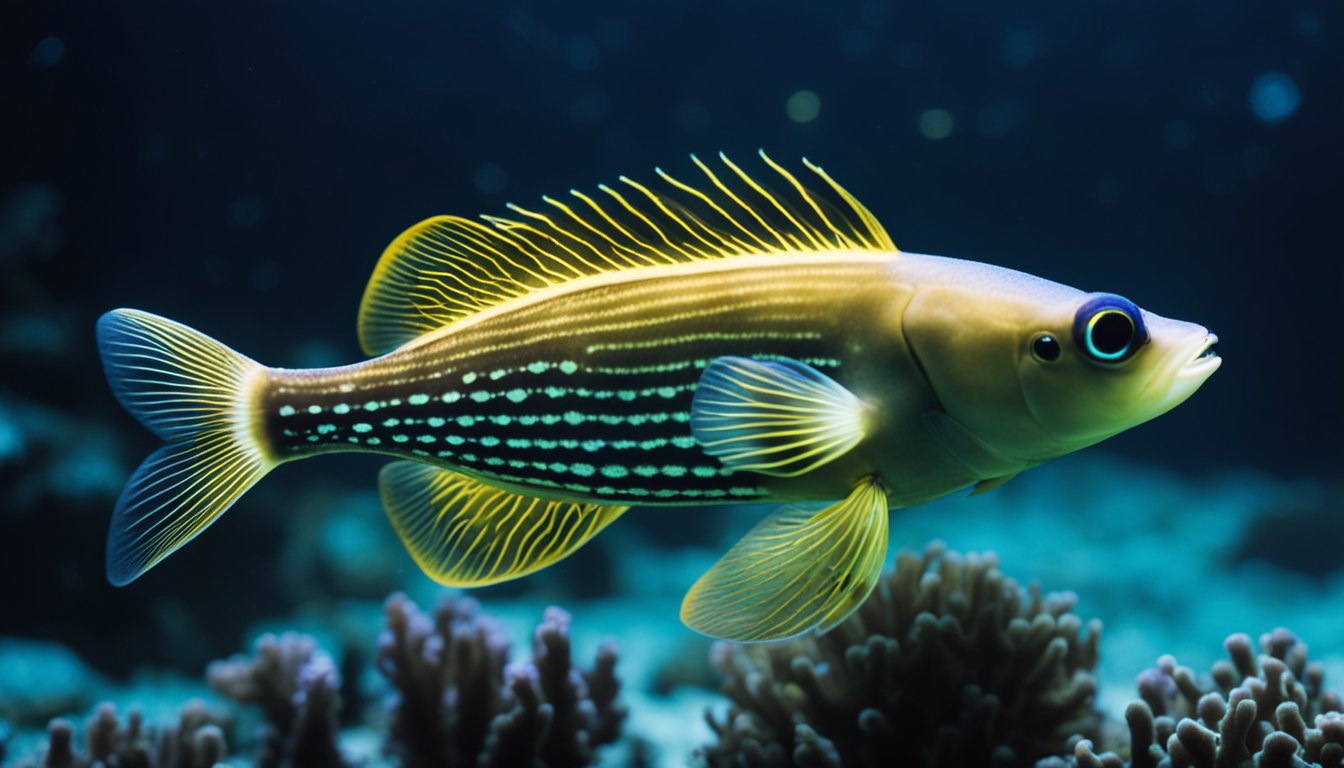
The ocean is home to a host of creatures, some of which are still a mystery to us.
One such creature is the lanternfish, a small fish that emits light in the depths of the ocean.
This light is not only used to attract prey but also to communicate with others of its kind.

Scientists have been studying the lanternfish and its unique light-producing abilities for years.
They have discovered that the fish has special organs called photophores that produce the light.
These photophores are strategically placed on the fish’s body, allowing it to create a variety of light patterns to attract prey or communicate with other lanternfish.
The study of the lanternfish and its light-producing abilities has led to a better understanding of the deep-sea ecosystem.
Scientists have found that the fish plays a crucial role in the food chain, as it is a primary source of food for larger predators.
Additionally, the study of the lanternfish has led to new advancements in bioluminescence research, which has the potential to be used in various fields such as medicine and technology.
The Mysteries of Lanternfish Bioluminescence
Lanternfish is a small, deep-sea fish that produces light. This fascinating ability is called bioluminescence, and it has puzzled scientists for years.
In this section, we will explore the science behind light production in lanternfish and the ecological role of bioluminescence.
The Science of Light Production
Lanternfish produces light through a chemical reaction that involves two molecules: luciferin and luciferase.
When these two molecules combine, they produce light. But how does this happen?
The answer lies in the specialized cells called photophores that are present on the lanternfish’s body.
These cells contain luciferin and luciferase.
When the fish wants to produce light, it sends a signal to these cells, which then release the two molecules.
The chemical reaction between luciferin and luciferase produces light, which is then emitted from the photophores.
Interestingly, the color of the light produced by lanternfish varies depending on the species.
Some species produce blue light, while others produce green or red light.
This variation in color is due to the different types of luciferin and luciferase present in the photophores.
Ecological Role of Bioluminescence
Bioluminescence is not just a cool party trick for lanternfish. It serves several important ecological roles.
Firstly, it helps lanternfish to communicate with each other.
They use light signals to attract mates, warn off predators, and coordinate group movements.
Secondly, bioluminescence helps lanternfish to camouflage themselves.
They can adjust the intensity and color of their light to match the ambient light in their environment, making them less visible to predators.
Finally, bioluminescence plays a crucial role in the deep-sea food web. Lanternfish is a primary consumer, feeding on small planktonic organisms.
The light produced by lanternfish attracts these organisms, making them easier to catch.
In turn, lanternfish is an important food source for larger predators such as squid and whales.
In conclusion, the bioluminescence of lanternfish is a fascinating phenomenon that has many scientific and ecological implications.
By understanding the science behind light production and the ecological role of bioluminescence, we can gain a deeper appreciation for this amazing fish and the complex ecosystem it inhabits.
Lanternfish Habitats and Species Diversity

Deep-Sea Environments
The Lanternfish is a fascinating deep-sea creature with a unique adaptation that allows it to produce light.
These fish are found in all of the world’s oceans, from the surface down to depths of 3,000 meters.
They are most commonly found in the mesopelagic zone, which is also known as the “twilight zone” due to the limited amount of sunlight that penetrates to this depth.
Lanternfish inhabit a variety of deep-sea environments, including the open ocean, seamounts, and hydrothermal vents.
They are also found in areas with high levels of oxygen, such as upwelling zones where cold, nutrient-rich water rises from the depths to the surface.
These environments provide the ideal conditions for the growth and survival of the diverse species of Lanternfish.
Species Adaptations
Lanternfish have evolved a variety of adaptations that allow them to survive in the deep-sea environment.
One of their most notable adaptations is their ability to produce light, which they use for communication, camouflage, and attracting prey.
The light is produced by special organs called photophores, which are located on various parts of their body.
In addition to their light-producing abilities, Lanternfish have also developed unique physical features to help them survive in the deep-sea environment.
They have large eyes that are adapted to low-light conditions, allowing them to see in the dark.
They also have a streamlined body shape that reduces drag and allows them to move efficiently through the water.
Furthermore, Lanternfish have developed a range of feeding strategies to cope with the limited food availability in the deep-sea environment.
Some species are herbivorous, feeding on phytoplankton and other small organisms, while others are carnivorous, preying on smaller fish and invertebrates.
In conclusion, the Lanternfish’s ability to thrive in a variety of deep-sea environments and its diverse range of adaptations make it a fascinating subject of study for marine biologists.
Its unique features and behaviors continue to spark curiosity and wonder about the mysteries of the deep sea.
Human Interactions and Research

Observation and Study Methods
The Lanternfish is a fascinating creature that has piqued the interest of many researchers.
Scientists have used various methods to observe and study these deep-sea creatures, including deep-sea submersibles and remotely operated vehicles (ROVs).
These tools allow researchers to capture high-resolution images and videos of the Lanternfish in their natural habitat.
In addition to visual observations, researchers have also used genetic and molecular techniques to study the Lanternfish.
By analyzing the DNA of these creatures, scientists can learn more about their evolutionary history and genetic diversity.
These methods have helped researchers understand the unique adaptations that allow the Lanternfish to thrive in the deep sea.
Conservation Efforts
As humans continue to explore and exploit the deep sea, it is important to consider the impact of our actions on the creatures that call it home.
The Lanternfish is no exception.
While there are currently no specific conservation efforts aimed at protecting the Lanternfish, researchers are working to raise awareness about the importance of preserving deep-sea ecosystems.
One way to protect the Lanternfish and other deep-sea creatures is to establish marine protected areas (MPAs).
MPAs are designated areas where human activities are restricted to protect the biodiversity and ecological processes of the marine environment.
By creating MPAs in areas where the Lanternfish and other deep-sea creatures are known to live, we can help ensure their survival for future generations.
In conclusion, the Lanternfish is a unique and fascinating creature that has captured the attention of researchers around the world.
By using advanced observation and study methods, scientists are gaining new insights into the biology and behavior of these deep-sea creatures.
As we continue to explore and exploit the deep sea, it is important to consider the impact of our actions on the Lanternfish and other deep-sea creatures.
By working together to protect these fragile ecosystems, we can help ensure their survival for generations to come.
Frequently Asked Questions

How does the lanternfish use bioluminescence to survive in the deep sea?
The lanternfish, like many other deep-sea creatures, uses bioluminescence as a means of communication, camouflage, and attracting prey.
The fish has specialized light-producing cells called photophores, which can be found all over its body.
By controlling the intensity and color of the light, the lanternfish can blend in with the surrounding water or produce flashes of light to attract its prey.
What recent findings have scientists made about deep-sea creatures like the lanternfish?
Recent studies have revealed that many deep-sea creatures, including the lanternfish, have unique adaptations that allow them to survive in the extreme conditions of the deep sea.
For example, the lanternfish has a high concentration of wax esters in its body, which helps it stay buoyant in the water.
Scientists have also discovered that deep-sea creatures have a slower metabolism and reproduce at a slower rate compared to their shallow-water counterparts.
Can you explain the role of the lanternfish in the ocean’s ecosystem?
The lanternfish is an important part of the ocean’s ecosystem as it serves as a food source for many larger predators.
Due to its abundance and wide distribution, the lanternfish is considered a keystone species in the deep sea.
Additionally, the lanternfish plays a crucial role in the ocean’s carbon cycle as it helps to transport carbon from the surface to the deep sea.
What are some of the unique adaptations of deep-sea animals like the lanternfish?
Deep-sea animals have many unique adaptations that help them survive in the harsh environment of the deep sea.
Some of these adaptations include bioluminescence, large eyes for detecting faint light, and the ability to withstand high pressures.
The lanternfish, in particular, has a transparent body that helps it blend in with the surrounding water, as well as a specialized swim bladder that allows it to adjust its buoyancy.
How do researchers study deep-sea organisms in their natural habitat?
Studying deep-sea organisms in their natural habitat can be challenging due to the extreme depths and pressures involved.
Researchers often use remotely operated vehicles (ROVs) or submersibles to explore the deep sea and collect samples.
They may also use specialized cameras and sensors to study the behavior and physiology of deep-sea creatures.
What impact do human activities have on deep-sea species such as the lanternfish?
Human activities, such as deep-sea mining and bottom trawling, can have a significant impact on deep-sea species like the lanternfish.
These activities can disrupt deep-sea ecosystems and destroy habitats, leading to declines in population sizes and biodiversity.
It is important for humans to consider the potential impacts of their actions on the deep sea and take steps to minimize their impact on this fragile ecosystem.